Despite all we’re told about sun protection, more than one third of adults admit to getting sunburned in the past year. While the immediate symptoms of a sunburn are only temporary, the long-term damage is permanent and can emerge years later. Read on for our guide to caring for sunburned skin, including the symptoms of sunburned skin, the stages of sunburned skin and how you can prevent it from occurring in the first place.
What Causes A Sunburn? | Why Are Sunburns Harmful? | Sunburn Stages | Symptoms | How To Protect Your Skin | Ingredients To Use
What Causes A Sunburn?
A sunburn is skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. When your skin is exposed to UV rays, it releases a pigment called melanin to protect itself. Melanin acts as a natural sunscreen by absorbing and redistributing the energy from UV rays. However, it can only provide so much protection – if you are spending too much time in the sun, your tan can quickly become a sunburn.
When you experience sunburn, your body produces chemicals called inflammatory mediators which increase blood flow in the affected area(s). This action produces a sunburn’s characteristic redness, warmth and swelling. While you may immediately notice a pink hue and rise in temperature, it takes up to 24 hours for a sunburn’s full effects to set in. In other words, don’t be surprised if your slight burn has turned 50 shades of red by day two.
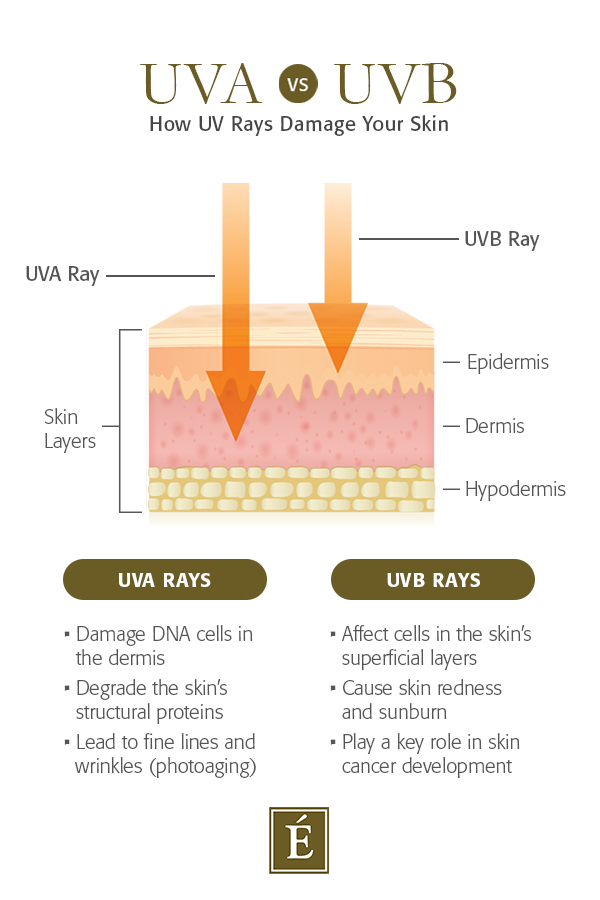
UVA Vs. UVB Rays
When it comes to UV radiation, there are two types of rays that cause skin damage: UVA and UVB. Here’s how they differ.
UVA Rays
UVA rays account for up to 95 percent of the UV radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface. They are present with equal intensity throughout the day and penetrate the skin more deeply than UVB rays. This type of radiation plays a key role in photoaging: It alters the DNA of cells in the dermis, causing damage to structural proteins like collagen and elastin. With a weakened structure, the skin begins to sag and develop fine lines and wrinkles.
UVB Rays
UVB rays cause damage in the skin’s more superficial layers and are responsible for skin reddening and sunburn. They are also more closely linked with the development of skin cancer. The intensity of UVB rays varies by season, location and time of day. These rays are at peak intensity between 10am and 4pm from April to October but have the potential to damage skin year-round. Unlike UVA rays, they cannot pass through glass and will reflect back towards the skin, hitting it twice and causing even more damage.
Why Are Sunburns Harmful?
So, why are sunburns so bad? Aside from their immediate pain and discomfort, sunburns also cause long-lasting damage to the skin. Sunburns contribute to premature aging in the form of fine lines, wrinkles, sagging skin and sun spots. They also play a major role in the development of skin cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, the risk for melanoma doubles if you have had more than five sunburns, and one in five Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70.
Sunburn Severity
Sunburns can range in severity, from mild burns that fade quickly to severe burns that can require a trip to the hospital:
Mild
Mild sunburns typically last between three and five days. They are accompanied by redness, tenderness and slight pain.
Moderate
Moderate sunburns tend to be more painful and can take up to two weeks to heal completely. They are characterized by vibrant redness, swelling, heat and small blisters.
Severe
Severe sunburns require a visit to a doctor. These burns are accompanied by red to purplish discoloration, large painful blisters and symptoms such as chills, nausea and dehydration.
Symptoms Of Sunburned Skin
The symptoms of sunburned skin include:
- Redness
- Pain and/or tenderness
- Heat
- Itchiness
- Swelling
- Small blisters
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is recommended that you visit a doctor:
- Fever
- Faintness
- Rapid pulse
- Nausea
- Chills
- Confusion
- Large, painful blisters
Risk Factors
Everyone reacts differently to sun exposure. There are several risk factors that can impact your susceptibility to sunburn:
- A fair complexion
- Freckles and/or red hair
- UV exposure between 10am and 4pm
- High altitudes
- Proximity to the equator
- Medications that cause photosensitivity
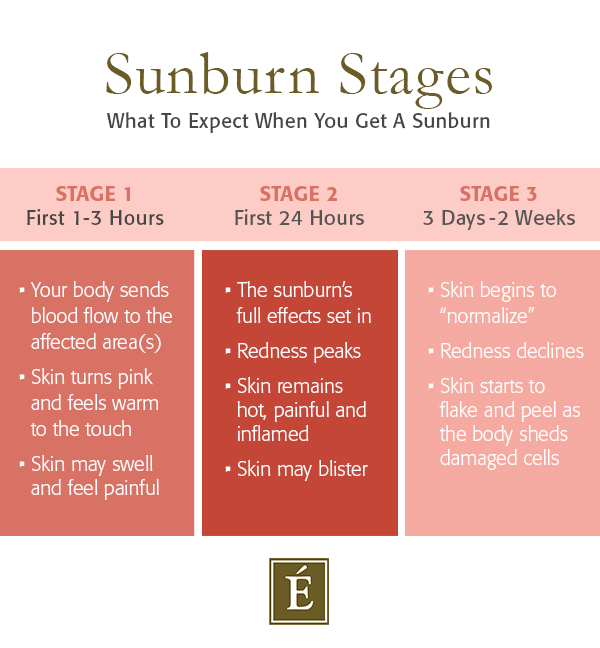
Stages Of A Sunburn
A typical sunburn follows three stages:
Stage 1: First 1-3 Hours
In the first few hours after sun exposure, your body reacts by increasing blood flow to the affected area(s). This inflammatory response causes the skin to become pink, swollen and warm to the touch.
Stage 2: First 24 Hours
It takes around 24 hours for the full effects of a sunburn to set in. As the skin continues to hold onto heat and discomfort, redness and pain peak and small blisters may begin to pop up on the skin’s surface.
Stage 3: 3-14 Days
The sunburn healing process can last from three days to two weeks. During this time, the skin begins to “normalize.” Redness, swelling and pain decline and the skin may become itchy as it starts to peel and flake.
Fun fact: Do you know why sunburned skin peels? Sun damage accelerates skin cell turnover, shortening the amount of time young cells usually have to mature and separate. As a result, they stick together like sheets of tissue paper that peel off over the course of healing.
How To Protect Your Skin
Luckily, there are several ways that you can protect your skin before, during and after sun exposure.
Before Sun Exposure
Rule number one of sun protection: Always apply a chemical or physical sunscreen. But, which one? Equally effective, they simply differ in their active ingredients and how they protect the skin. Chemical sunscreens are “absorbers” that convert UV rays into heat before releasing them from the skin. Physical sunscreens create a protective barrier that blocks and reflects UV rays before they make contact with the skin’s surface. Whether you decide to go the chemical or physical route, we recommend reaching for a broad-spectrum formula that will protect against both UVA and UVB rays.
What about SPF? SPF stands for “Sun Protection Factor” and measures how long your skin will be protected from UVB rays (and by extension, sunburn). For extended sun exposure, The Skin Cancer Foundation advises an SPF of 30, a protective factor which filters out 97 percent of the sun’s UV radiation. Apply at least one teaspoon of sunscreen for each area of your body to keep it sufficiently protected – and don’t skip over easily forgotten areas like the tops of the ears, the back of the neck and the hands and feet. Our Lilikoi Mineral Defense Sport Sunscreen SPF 30 is a great option if you’re active outdoors and Lilikoi Daily Defense Moisturizer SPF 40 works well for everyday use.
During Sun Exposure
Sun care doesn’t stop once you’ve applied sunscreen. To avoid sun damage, it’s crucial that you continue to protect your skin throughout the day. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
- Seek shade between the hours of 10am and 4pm, when UV rays are at their most intense.
- Beware reflective surfaces: Water, snow and sand reflect UV rays and increase the risk of sunburn.
- Cover up with a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses and sun-protective clothing with a UPF (Ultraviolet Protective Factor) 40 or more.
- Reapply sunscreen at least every two hours, or after 40 minutes if you’re swimming or sweating.
- Head indoors at the first sign of sunburn.
After Sun Exposure: What Helps Sunburn?
We’ve all been there: You nod off at the beach, spend a few too many minutes by the pool or forget to keep track of your sunscreen application. The moral of the story is: Even if you follow the steps above, there’s no guarantee you’ll end the day sunburn-free. Here’s what to do when you get a sunburn.
Stay Hydrated: Inside & Out
Dermatologist Whitney Bowe, MD tells HuffPost: “Bad sunburns cause a process called vasodilation, where your blood vessels dilate and you lose water from your skin very quickly.” To counteract the drying effects of a sunburn, you should drink plenty of water and load up on hydrating fruits and vegetables like cucumber, watermelon and cantaloupe.
Cool Your Skin Down
Another sunburn relief tool is a cool bath or shower to soothe redness and dryness – but skip the soap, which can irritate scorched skin. If cool water isn’t cutting it, apply a cold compress to the burn. Pour water and ice into a bowl, soak a cloth in the liquid and hold it over the burn. Each of these methods will help absorb heat from your skin and minimize swelling.
Soothe & Repair Red, Dry Skin
Sunburn can leave your skin red, dry and raw. To repair dryness, reach for moisturizing oils and lotions that include soothing ingredients such as rosemary, arnica and rosehip. And, steer clear of products containing petroleum, an ingredient that can lock in heat and exacerbate your symptoms.

Don’t Pick Your Skin
Hands off! It may be tempting, but don’t pull at, pick or exfoliate your sunburned skin. Why? It’s already shedding on its own. As your skin heals, healthy skin cells rise to the surface and the sun-damaged cells naturally flake and peel off. These new cells are delicate and susceptible to irritation: Picking and prodding will only make your sunburn look and feel worse and extend the time it takes the affected skin to heal.
Apply A Vitamin C Serum
One of the key culprits of premature aging is sun exposure. UV rays promote the production of free radicals, unstable and highly reactive molecules that cause damage to structural proteins like collagen and elastin. Without a stable structure, skin loses the volume, density and bounce associated with a youthful complexion.
You can minimize the visible signs of sun exposure by adding a Vitamin C serum to your skin care routine. Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps protect cells from free radical damage. It also promotes collagen production in the skin, helping to minimize the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Get A Full Body Treatment
If slathering your skin in aloe vera isn’t doing the trick, book a professional body treatment at your favorite spa. Many spas offer after-sun services designed to cool and calm red, dry skin.
Tip: When you book your appointment, be sure to mention that you are suffering from sunburn so your esthetician can customize your treatment accordingly.
Ingredients You Should Use To Treat Sunburn
Our Product Support Team recommends the following ingredients and products if you’re dealing with sunburn.
Aloe Vera
The gel of the aloe vera plant has been used for centuries to treat burns, cuts and skin dryness. Aloe vera gel and juice contain restorative properties that can be beneficial for all types of thermal burns (injuries caused by temperature changes), including sunburn and frostbite.
Botanical Hyaluronic Acid
To treat both face and body, consider a product that uses botanical hyaluronic acid, designed to soothe dry, irritated skin. This ingredient delivers intense hydration thanks to its multi-molecular weight, which absorbs into the skin, delivers deep hydration and preserves moisture. Its hydrating power leaves the skin glowing and youthful looking.
Vitamin C And E
Vitamins C and E are important for sun damage skin relief and recovery. Vitamin C is an antioxidant which fights free radical damage, preventing damage caused by UV rays. Vitamin E visibly diminishes the appearance of wrinkles and uneven skin texture. Look for a skin care product that features both vitamins! Firstly, stabilized Vitamin C delivers optimal antioxidant benefits to improve the skin’s appearance. And second, Vitamin E reduces the appearance of sun damage, fine lines and wrinkles.
Chamomile
Chamomile calms and balances skin’s appearance. According to Byrdie, chamomile has “anti-inflammatory properties” and protects against “long-term and short-term skin inflammation.” Look for skin care options that contain this ingredient to improve the appearance of damaged and dry skin.
Stone Crop
Stone crop is a succulent that thrives in hot and dry desert conditions. These plants retain moisture for extended periods because they have adapted to receiving limited amounts of water and store a high amount of water content in their leaves. In skin care, stone crop provides hydration and also can soothe dry skin from sun damage.
Echinacea
Echinacea is a group of flowering plants loaded with plant compounds that function as antioxidants. Antioxidants include flavonoids, cichoric acid and rosmarinic acid, which are said to protect and repair dry, damaged skin, as well as give it a more taut and firm appearance. If you’re dealing with sunburnt skin, consider a product with echinacea, which will help provide relief.
Coconut Oil
Does coconut oil help sunburn? It has been used as a natural medicinal treatment for thousands of years. Today we understand that coconut oil is a moisturizer and antioxidant that restores the skin’s moisture barrier and contains antiviral, antifungal and antibacterial properties. A skin care product formulated with coconut oil will improve the appearance of dry, dehydrated and sun damaged skin.
How do you protect your skin from the sun? Share your thoughts with us in the comments and join the conversation on social media.
This article was originally written in August 2019.
Adblock test (Why?)
Powered by WPeMatico
